Nigeria Economic Structure
Please note that we are not authorised to provide any investment advice. The content on this page is for information purposes only.
Nigeria Economic Structure: GDP Composition
Nigeria’s economic structure is largely oil-based. The economy has stumbled for years due to political unrest, corruption and poor fiscal policies. However, since the restoration of democracy and introduction of economic reforms, the country is growing at a fast pace. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projections, Nigeria is the second fastest growing economy in the world and will outperform other African economies in the near future.[br]
Nigeria Economic Structure: GDP Composition
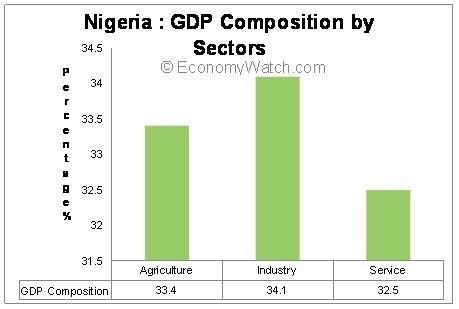
Agriculture was central to Nigeria’s economic structure till the early 1990s. It was one of the main sources of foreign currency. However, over the years, the agricultural sector has become a grey area for the Nigerian economy. According to the 2009 estimates, the sector provides employment to more than 70% of the working population but contributes only 33.4% of the total national production. The country has not been able to satisfy internal demand and has to import a considerable amount of food products.
The Nigerian industrial sector primarily depends on oil extraction and refining. It employs approximately 10% of the labor force and accounts for 34% of the GDP. The service sector is also gradually emerging in the country. Almost 20% of the population is engaged in service sector jobs. This sector contributes 32.5% of the total GDP.
Nigeria Economic Structure: Business Climate[br]
Nigeria’s economic structure suffers from a lack of infrastructure and poor regulation related to foreign and private investments. To encourage foreign direct investment in the oil and natural gas sector, the country has aligned trade tariffs with the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) standards. Prior to 2005, trade tariffs were the second largest source of revenue for the country.
In the non-oil economy, there are several unexplored segments, such as the telecommunication and service sectors. However, to enjoy long term benefits, foreign investors must educate themselves about the local culture, traditions and trade laws.