Indonesia Economic Structure
Please note that we are not authorised to provide any investment advice. The content on this page is for information purposes only.
Indonesia’s economy has weathered a global economic downturn twice (1997-98 and 2008). The economy vastly relies on the agriculture, manufacturing and services sectors for growth. Due to several natural disasters, political and social disturbances and terrorist activities, the economy has been through significant changes in the last few decades. These also led to less development employment opportunities, forcing a big chunk of the population to find employment in neighboring nations, especially Malaysia.[br]
Indonesia’s economy has weathered a global economic downturn twice (1997-98 and 2008). The economy vastly relies on the agriculture, manufacturing and services sectors for growth. Due to several natural disasters, political and social disturbances and terrorist activities, the economy has been through significant changes in the last few decades. These also led to less development employment opportunities, forcing a big chunk of the population to find employment in neighboring nations, especially Malaysia.[br]
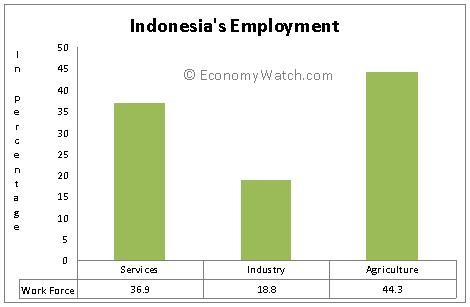
The graph below shows the breakup of the 95 million-strong workforce into the three major sectors of Indonesia’s economic structure:
Indonesia Economic Structure: Major Sectors
The major economic sectors of Indonesia are as follows:
Primary Sector: While being the biggest employment sector of the country, agriculture includes three types of farming. These include smallholder farming, irrigated rice terraces and smallholder cash cropping. Some of the major produce of Indonesia includes rice, tea, coffee, cocoa, spices, rubber, copra, peanuts, eggs, pork, poultry and palm oil. Some crops are cultivated mainly due to the even distribution of rainfall and consistent monsoon climate in Indonesia. The country is the fourth largest producer of rice and coffee in the world. It exported 271,000 tons of coffee in 2007.
Secondary Sector: The manufacturing sector of Indonesia contributes 27.9% to the country’s GDP. The industrial production rate in the country stood at 2% as of 2009. Some of the major industries in the country are as follows:
|
Industry |
Value (as of 2006) in Million Rupiahs |
|
Petroleum refinery industry
|
119,833,900 |
|
Liquefied natural gas
|
53,791,300 |
|
Textile, leather products and footwear |
90,871,700 |
|
Wood and wood products
|
44,410,400 |
|
Paper and printing products
|
39,968,900 |
|
Cement and non-metallic quarry
|
29,015,100 |
|
Iron, steel and other basic metals
|
20,492,200 |
|
Transport equipment, machinery and apparatus |
221,891,800 |
|
Other manufacturing industries |
7,148,300 |
[br]
Tertiary Sector: With 38.5% contribution to the country’s GDP, the services sector remains a pillar of Indonesia’s economy. The value of the country’s banking system stood at $220-billion as of 2008. The growing IT services sector was impacted to some extent by the global economic downturn in the late 2000s. However, there are expectations of about 15% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the period of 2010-2014. The country’s hospitality industry is a big booster of the economy. According to the Tourism and Culture Ministry, there were 493,799 tourist visits in September 2009 alone, despite the recession.