Cameroon Economic Structure
Please note that we are not authorised to provide any investment advice. The content on this page is for information purposes only.
Cameroon economic structure has several indicators that correspond to those of developing nations. The country relies on bountiful mineral resources and favorable agricultural conditions. However, fund mismanagement and overvalued currency are the biggest impediments to Cameroon’s economic growth.[br]
Cameroon economic structure has several indicators that correspond to those of developing nations. The country relies on bountiful mineral resources and favorable agricultural conditions. However, fund mismanagement and overvalued currency are the biggest impediments to Cameroon’s economic growth.[br]
Cameroon Economic Structure: GDP Composition
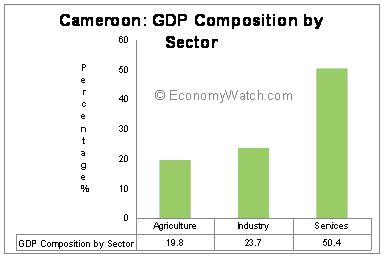
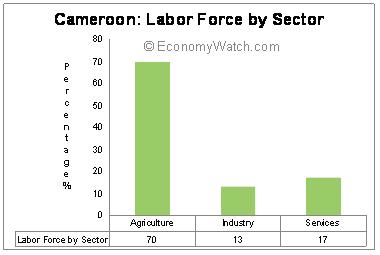
Agriculture is the most important component of the Cameroon economic structure. It contributes approximately 20% to the GDP share and engages the majority portion of labor force (70%). Industrial sector provides for almost 29.7% of the GDP while providing employment for 13% of the working population.
With the diversification of the economy, service sector is also gradually emerging in the nation. As per 2009 statistics, the service sector employs almost 17% of the total working population and contributes above 50% to the annual GDP figures.
France is the largest trade partner of Cameroon. The country also has bilateral trade and investment relations with the US. The US has an agreement of $1 million with the nation. It is the largest importer of Cameroon’s oil.
Cameroon Economic Structure: Business Environment[br]
Till the 1990s, Cameroon had a closed economy with strict regulations against private and foreign investors. During early 1990s, IMF and World Bank provided financial assistance to the country. This led to a series of economic reforms that brought Cameroon’s economy in sync with the global standards. These reforms strategically focused on increasing agricultural productivity, stimulating business investment and restructuring the banking sector.
Despite ongoing reforms, the Cameroon economy is relatively closed. The country ranks one of the lowest in terms of Doing Business Index. International organizations are pressing the government for greater economic reforms and ensuring transparency in fund administration. In 2008, Cameroon entered into agreements with the IMF, which calls for better managed economic adjustment policy. This initiative is named as the ‘Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility.’