Bahrain Economy
Please note that we are not authorised to provide any investment advice. The content on this page is for information purposes only.
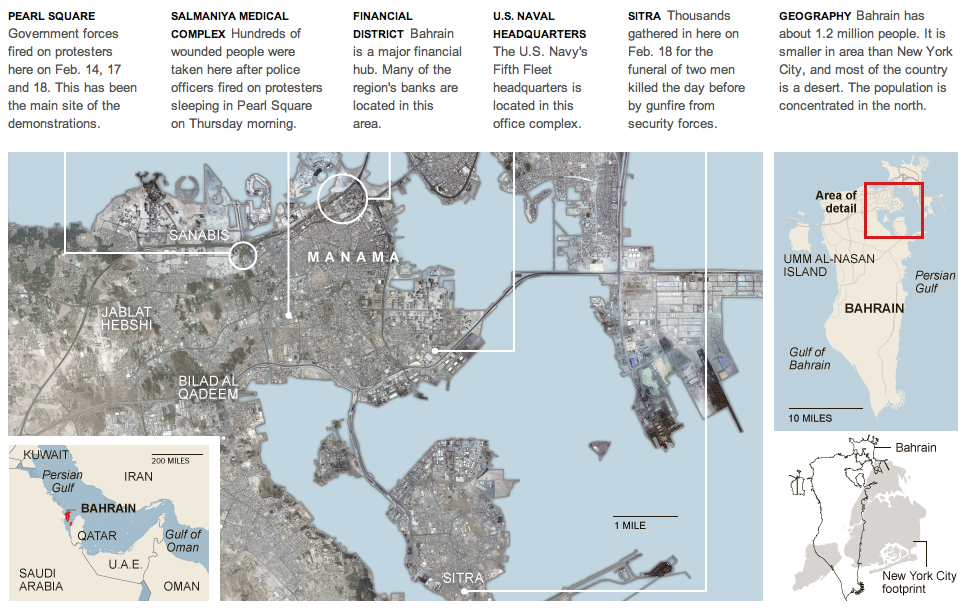
The Kingdom of Bahrain is an archipelago of 33 islands located near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. Bahrain’s capital, Manama, resides on the Northeast tip of Bahrain Island; the largest island in the kingdom. Bahrain is strategically positioned in the Middle East with good access to its neighbouring countries in the region by air, land and sea.
The Kingdom of Bahrain is an archipelago of 33 islands located near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. Bahrain’s capital, Manama, resides on the Northeast tip of Bahrain Island; the largest island in the kingdom. Bahrain is strategically positioned in the Middle East with good access to its neighbouring countries in the region by air, land and sea.
Bahrain is next to Saudi Arabia, the largest market in the region that serves as a hub for services and trade between the Middle East and the rest of the world. Bahrain also lies in the middle of the oil shipping route between the Middle East and the West.
Bahrain, like many Gulf States has historically relied heavily on oil as a primary source of income. However, with oil reserves forecasted to run dry in the next 10 to 15 years, the Bahraini government has acted on the need to diversify its economy and reduce the country’s dependence on oil.
Table of Contents
Bahrain’s Industry and GDP
Today, Bahrain’s service industry contributes 41.5 percent to GDP. The finance and tourism industry have also been critical elements to Bahrain’s economic diversification. The finance industry alone is responsible for nearly 27 percent of GDP and 40 percent of Bahrain’s economic growth in 2011. In 2010, Bahrain’s GDP grew of 3.955 percent and GDP (PPP) to US$29.663 billion.
Bahrain has emerged as a major financial centre, especially in the areas of Islamic banking and financial services. Another key factor to Bahrain’s economic sustainability has been the privatisation of its economy. At present, the private sector accounts for more than half of Bahrain’s GDP.
Bahrain’s involvement in the economy is attributed to the state’s connections to large public corporations such as Bapco (oil, 37 percent stake in shares), Alba (aluminum, 77 percent), Gulf Air (national carrier, 50 percent) – as well as a 50 percent stake in the National Bank of Bahrain.
The Bahraini government has however, stated its intentions to sell parts of its shares in these companies, at the same time implement new reforms in the public sector to convert the government’s role as an operator to a regulator. Nevertheless, the oil industry remains a critical element of Bahrain’s economy, with petroleum production and refining accounting for over 60 percent of Bahrain’s exports and over 70 percent of the government’s earnings.
Bahrain’s oil production has gradually dropped from 48,610 barrels/day in 2007 to 48,520 barrels/day in 2010. The country’s primary purpose for economic diversification has been to reduce its reliance on oil, and its unemployment figures.
Unemployment in Bahrain
2005 data by the IMF reports Bahrain’s unemployment rate at 15 percent. However a 2010 article by the Gulf News, quoting Bahrain’s labour minister Majeed Al Alawi, stated unemployment rates in Bahrain had fallen to 3.7 percent in 2010. While unemployment has fallen, current turmoil in Bahrain stems from the Shiite Muslim majority who believe they face discrimination in finding jobs compared to the ruling Sunni minority.
Bahrain’s labour force is made up of 611,000 people with 44 percent of them being non-nationals or expatriates. The number of expatriates has declined in recent years since sponsorship for expatriate workers was reduced by the government. Increasing the cost of employing foreign labour placed more emphasis on hiring local Bahrainis.
Bahrain’s Trade and Economy
Bahrain is the 10th freest economy in the world and the freest economy in the Middle East according to the 2011 Economic Freedom Index. Bahrain’s overall score of 77.7 was 1.4 points higher than the previous year, with improvements in trade freedom, investment freedom, labour freedom, and freedom from corruption.
Bahrain has also been able to secure numerous bilateral trade and economic agreements with more than 40 countries including China, France, India, Singapore and the United Kingdom. The most prominent of which is the United States-Bahrain Free Trade Agreement (USBFTA) which doubled trade between the two nations between 2005 and 2008.
The USBFTA was also partly responsible for the FTA Actualization for Bahrain (FAB) program that seeked to stimulate private sector activity towards the US market through technical assistance, export marketing and promotion assistance to small and medium enterprises in Bahrain.
In 2010, the value of exports from Bahrain was US$15.13 billion, imports were estimated at US$12.13 billion. Primary recipients of Bahrain’s exports include India (4.2 percent) and Saudi Arabia (2.78 percent). Bahrain’s primary import partners include Saudi Arabia (22.91 percent), France (9.76 percent), US (7.95 percent), China (6.4 percent), South Korea (5.26 percent), Japan (5.19 percent), Germany (5.01 percent) and the United Kingdom (4.34 percent).
Bahrain’s current account balance in 2010 doubled from the previous year, rising from US$0.56 billion in 2009 to US$1.12 billion and is expected to continue rising in the next five years from US$1.343 billion in 2011 to US$2.433 billion in 2015.
Read more on Bahrain’s economy, including forecasts and trade statistics on EconomyWatch below.