Kenya Economic Structure
Please note that we are not authorised to provide any investment advice. The content on this page is for information purposes only.
Kenya economic structure is highly dependent on agricultural production. Since independence, the country has received considerable foreign aid, although the industrial sector still remains underdeveloped. As a result, the country has to import a majority of its consumer goods.[br]
Kenya economic structure is highly dependent on agricultural production. Since independence, the country has received considerable foreign aid, although the industrial sector still remains underdeveloped. As a result, the country has to import a majority of its consumer goods.[br]
Kenya Economic Structure: GDP Composition
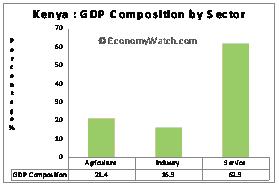
The service sector is the largest contributor to Kenya’s GDP. It accounts for approximately 62.3% of the annual GDP volume (as per 2009 data). Agriculture contributes almost 21% to the country’s GDP, although the sector engages more than 75% of the working population. Kenya’s major agricultural produce includes tea, coffee, wheat, sugarcane, fruits, vegetables and dairy products. Traditional methods of agriculture and over reliance on the weather conditions have impacted productivity since 1997.
The industrial sector accounts for only 16% of the country’s GDP. The service sector and the industrial sector provide employment to 25% of the working population. The major industries include horticulture, oil refining, cement, tourism, ship repairing and small-scale consumer goods manufacturing.
Kenya Economic Structure: Business Climate
Kenya’s economic structure has been favorable to private and foreign investment since independence. However, some of the previous governments imposed restrictions on foreign investment to promote the ‘Africanization’ of trade. In 1993, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) singed an economic reforms agreement with Kenya. As part of the agreement, Kenya removed subsidies, trade restrictions and the liberalized business climate in the country. In 2004, the government also removed non-tariff trade barriers and the integrated customs union according to international standards.[br]
The country receives significant international donations for developmental and budgetary support. The IMF and World Bank have also provided huge sums of money for the development of infrastructure and to curb corruption at the administrative levels. The US is one of the major donors to Kenya. Under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), the US provides donations to Kenya’s apparel industry.