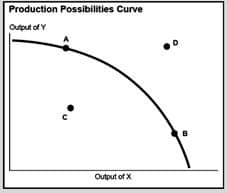
Economic Graphs and Charts
Economic graphs are related to economics, which is a branch of social science that is concerned with money flow patterns, trade activities and industrial production in a state. Analyzing and understanding these economic patterns require an in-depth scientific approach. This further involves interpretation of theories that are based on trends and data. No wonder, economists use economic graphs and charts to represent complex data in pictorial format.